Review the following images with JABS technique
and provide your likely diagnosis.
JABS - Overview
Joints
Alignment
Bone
Soft tissue
Likely Diagnosis:
Note that a final diagnosis will depend upon clinical findings and laboratory results in many cases.
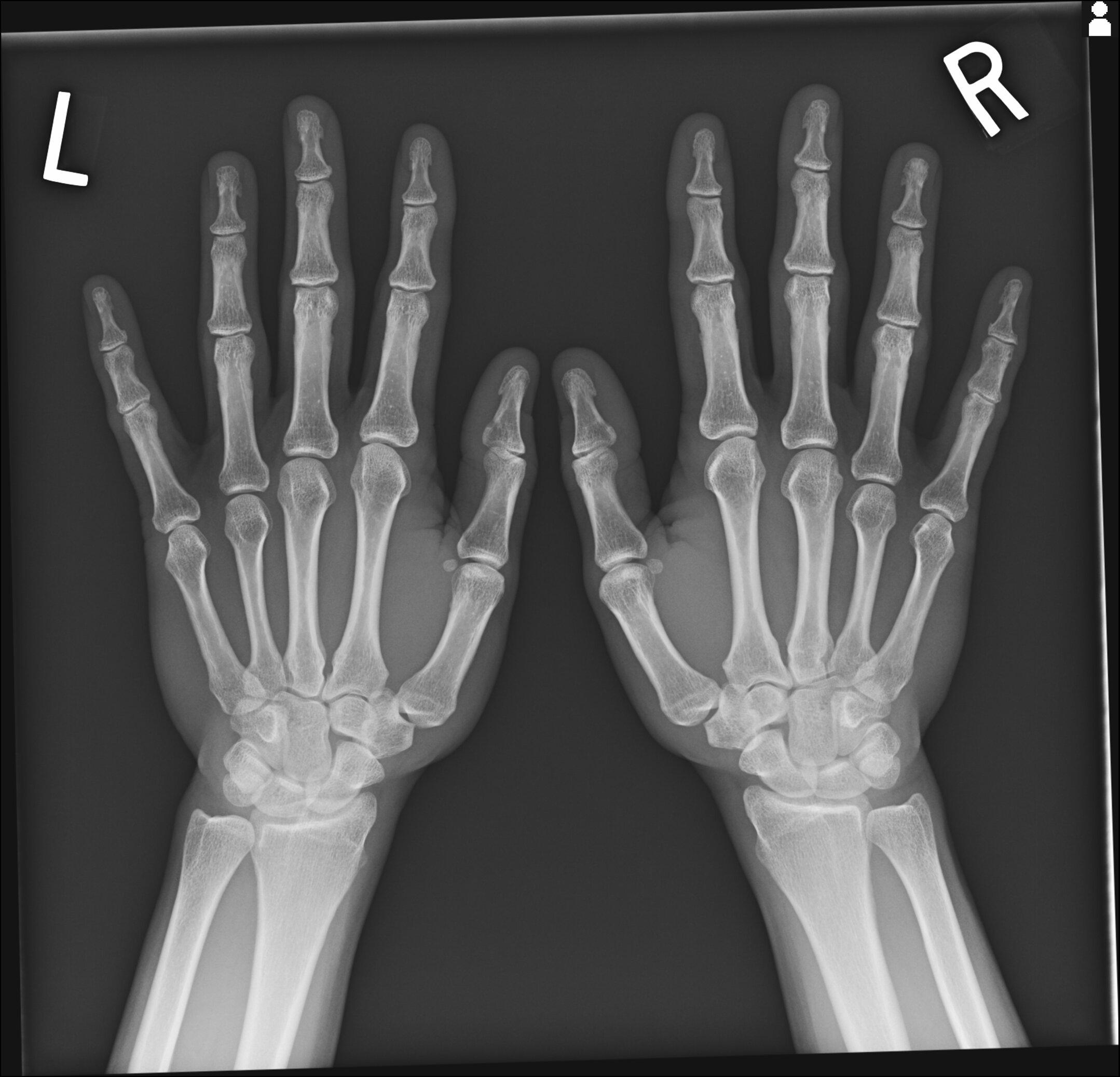
Case 1
JABS Review
Joints:
- Joint space loss at DIPJs most pronounced at the left 3rd DIPJ, with central erosions (2nd DIPJs) and osteophytosis, “gull-wing” appearance
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Normal
Soft tissue:
- Mild soft tissue swelling bilateral 2nd and 3rd DIPJs
Erosive osteoarthritis
Teaching Point: Classic “gull-wing” pattern of erosive OA
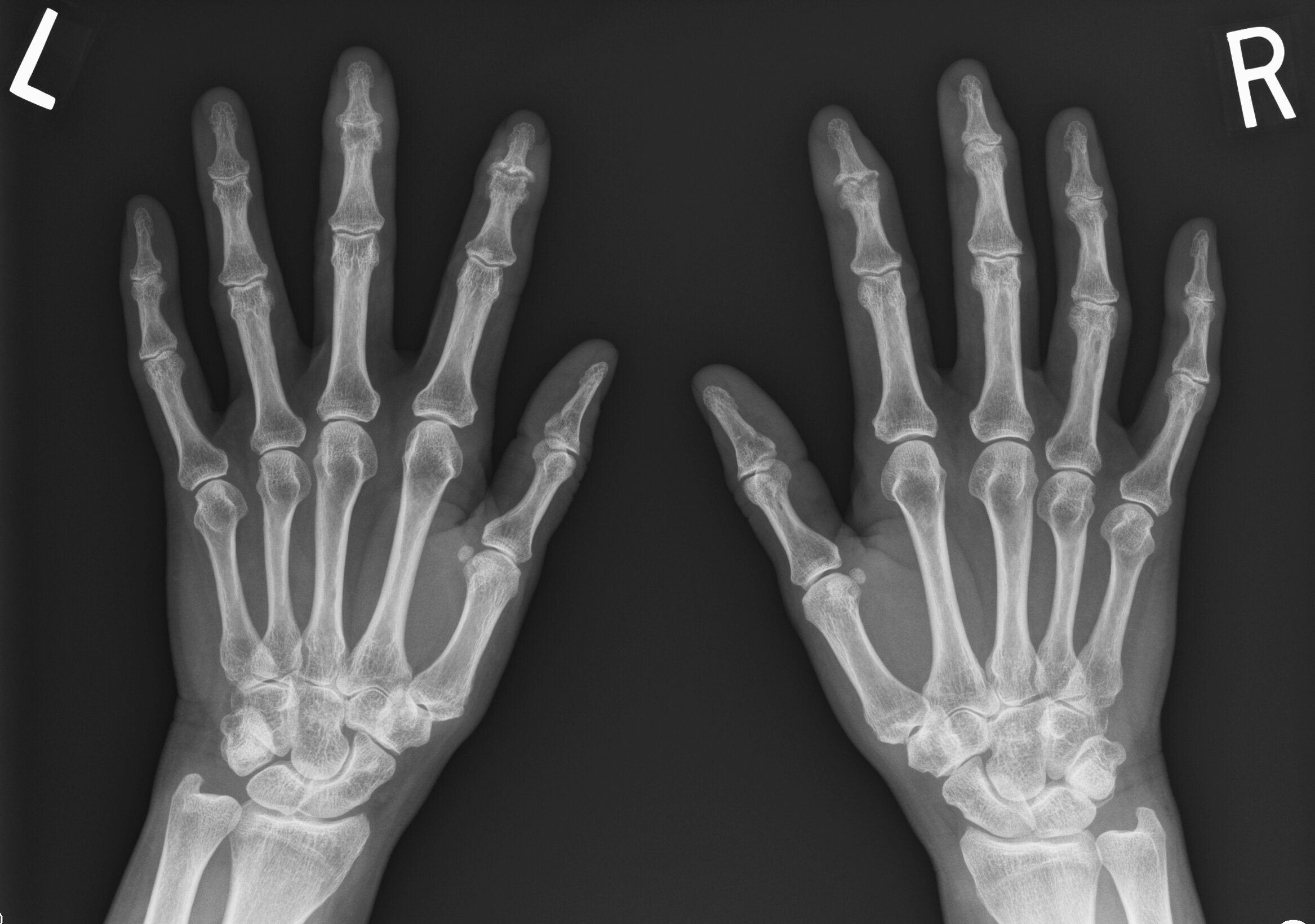
Case 2
JABS Review
Joints:
- Bilateral erosive disease, central and marginal, right 1st IP, 4TH & 5TH DIPJs, left 2nd, 4th & 5 DIPJs, 5th PIPJ.
- Small marginal erosions at right 1st MCPJ, 5th PIPJ, left 5th MCPJ.
- Associated joint space loss, also evident at the 2nd and 3rd MCPJs bilaterally.
- No chondrocalcinosis.
Alignment:
- Radial subuxation right 1st IP and left 5th DIPJ
Bone:
- New bone formation left ulnar styloid process and right 1st IPJ.
- No periosteal reaction or periarticular osteopenia.
- Chondrocalcinosis
Soft tissue:
- Mild diffuse soft tissue swelling digits, most pronounced left little finger in keeping with dactylitis.
Psoriatic arthritis
Teaching Point: Involvement DIPJ erosive disease and new bone formation suggests seronegative disease, dactylitis suggests PsA
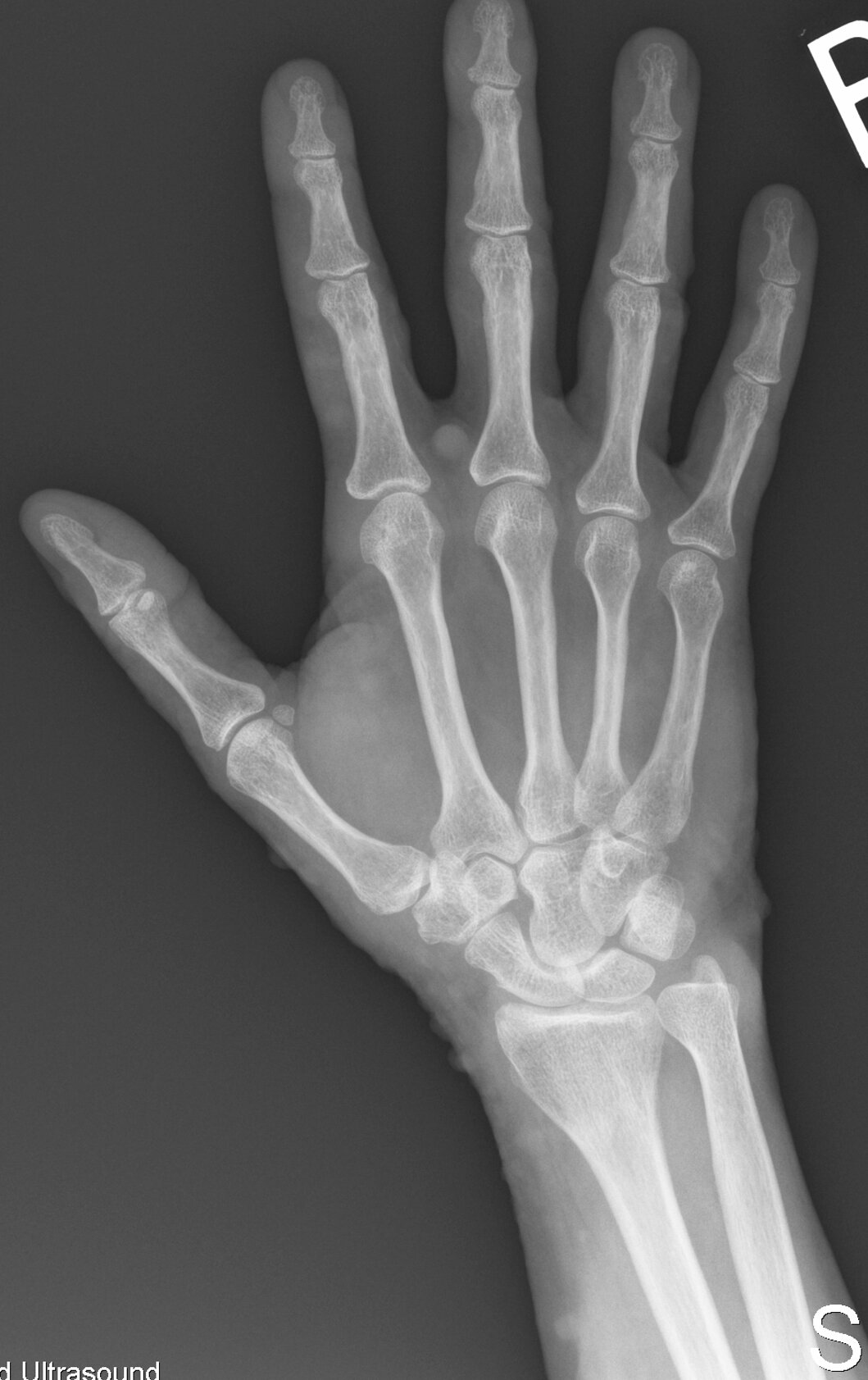
Case 4
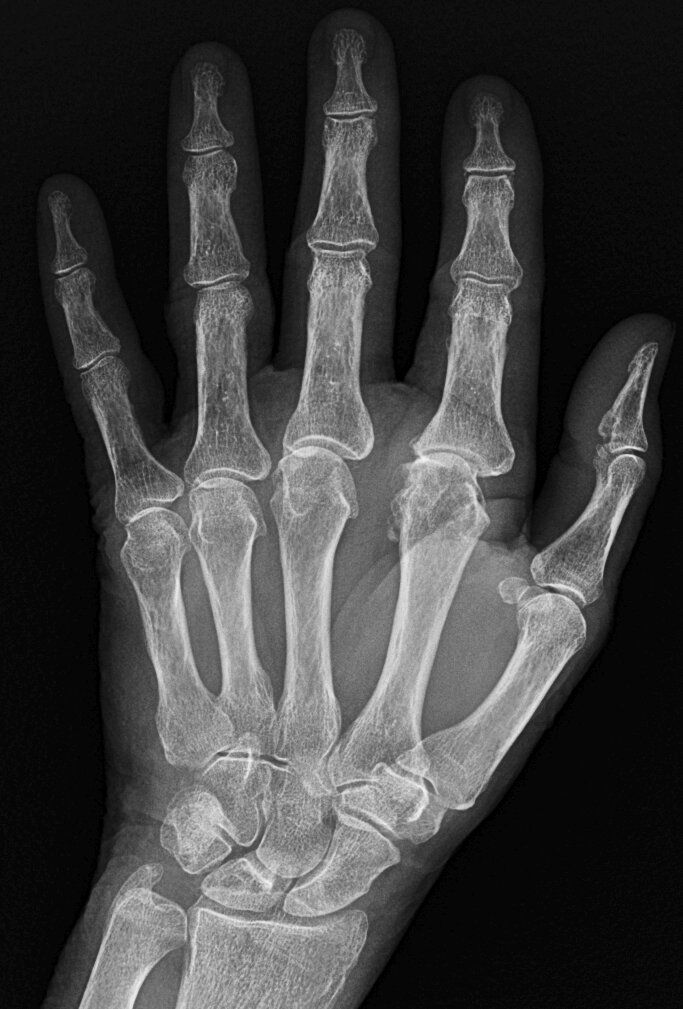
JABS Review
Joints:
- MCPJ joint space loss, most pronounced at the second and third 2nd and 3rd mcpj which also demonstrate osteophytes
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Normal
Soft tissue:
- Subtle calcification lunotriquetral ligament
CPPD arthropathy
Teaching Point:
- Chondrocalcinosis TFC is classic but remember that may not be radiographically visible in joint involved.
- Check ligaments as in this case.
- The majority of patients with CPPD arthropathy demonstrate chonedrocalcinosis of the wrist (TFC), symphysis pubis (articular disc) or knees (menisci and articular cartilage)
 info_outline
info_outline
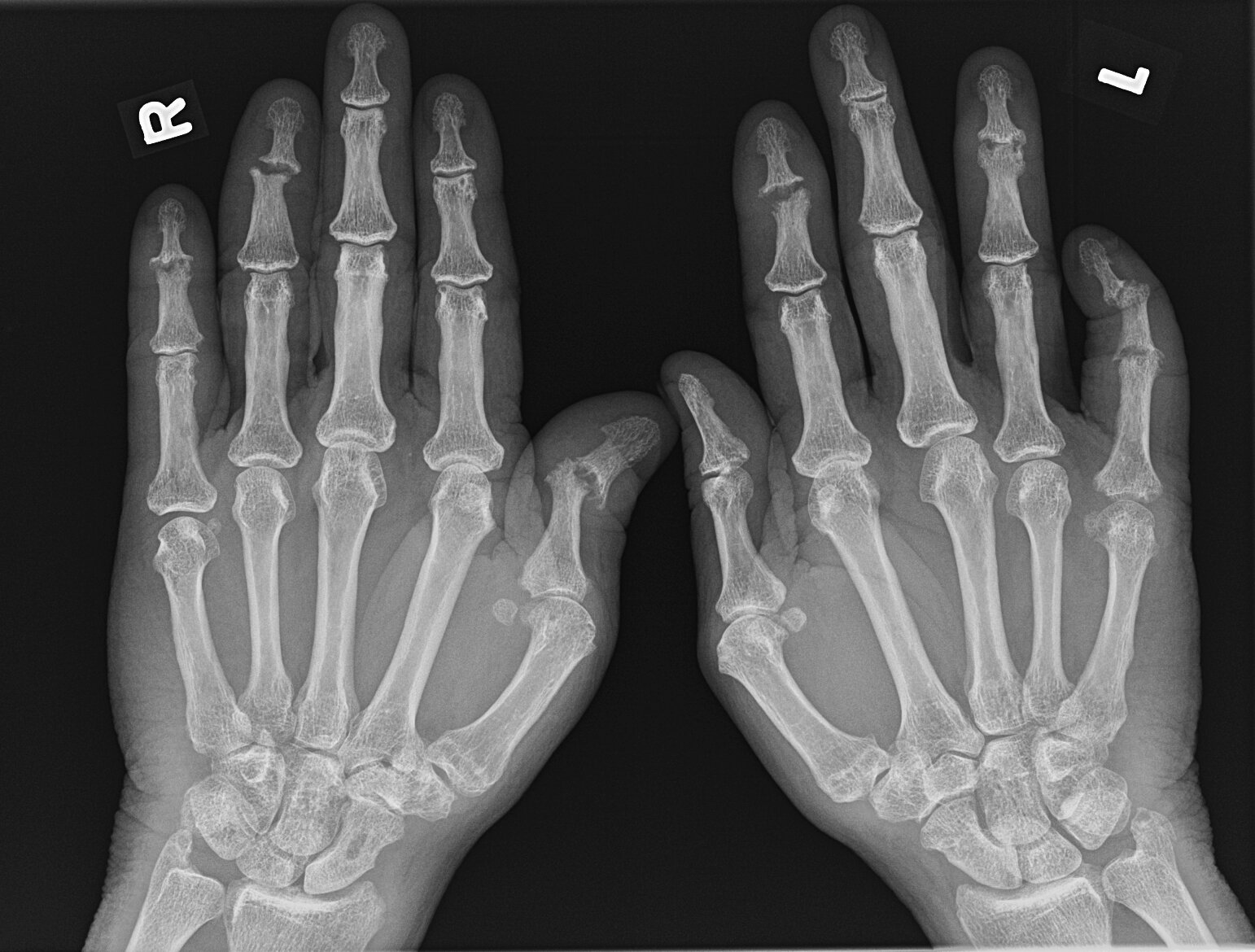
Case 5

JABS Review
Joints:
- Uniform joint space loss right 2nd DIPJ
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Early new bone formation bilateral 1st, right 2nd and 3rd tufts, right 3rd DIPJ.
- Early resorption right 3rd tuft.
- Incidental prior trauma left 2nd tuft and right 5th metacarpal neck
Soft tissue:
- Soft tissue swelling right 2nd DIPJ.
Seronegative arthritis, most likely Psoriatic arthritis
Teaching Point: New bone formation suggests seronegative arthritis
Case 6
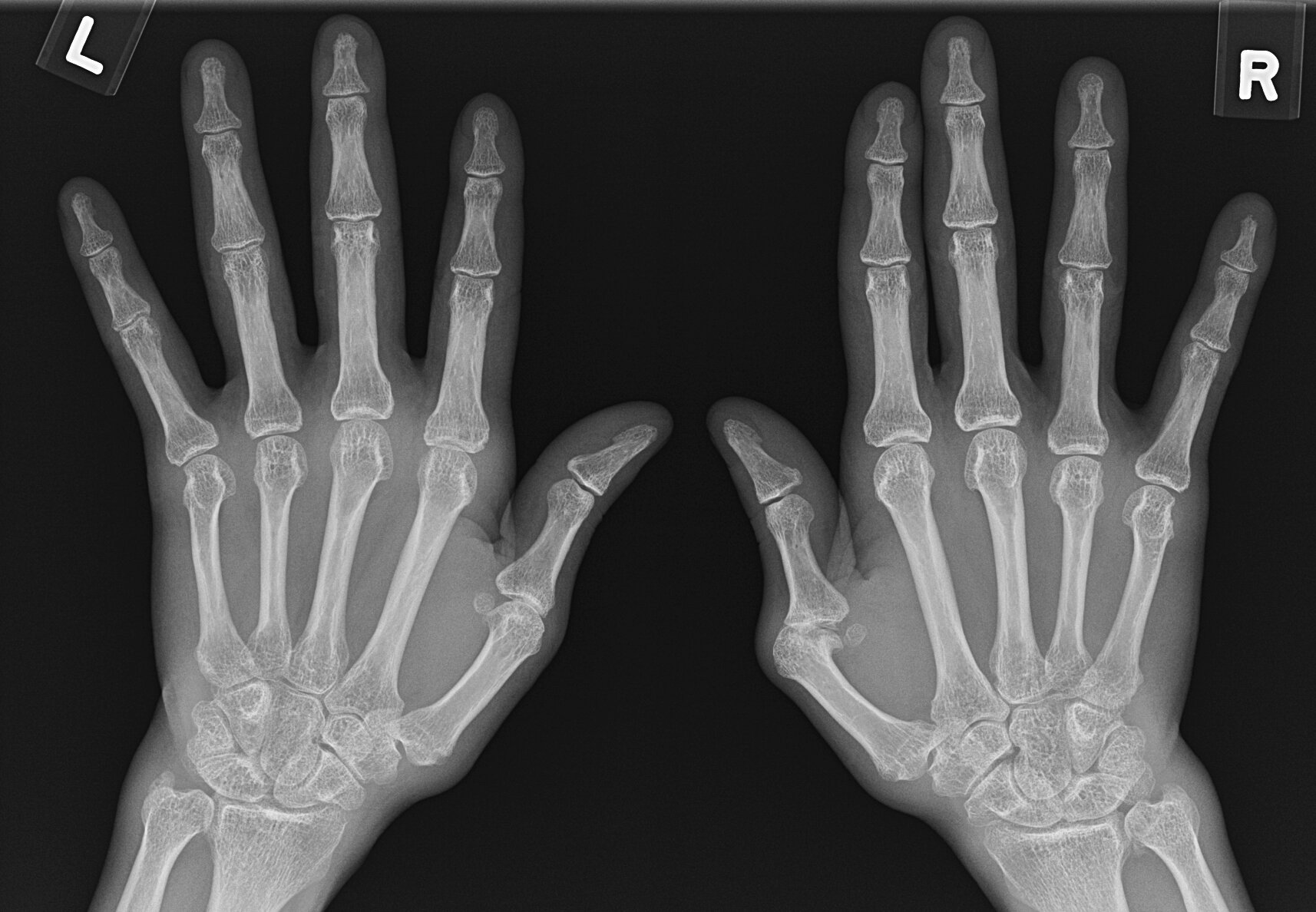
JABS Review
Joints:
- Minute marginal erosion left 2nd MCPJ and early erosion left ulnar styloid process
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Early acro-osteolysis bilateral 3rd and right 5th tufts
Soft tissue:
- Bilateral soft tissue swelling over the ulnar styloids and left 2nd, 3rd and right 2nd MCPJs
Scleroderma
Teaching Point:
- Soft tissue swelling over the ulnar styloids suggesting ECU tenosynovitis, is a common finding in inflammatory arthritis, particularly in rheumatoid arthritis and this case could be mistaken for early RhA except for evidence acro-osteolysis and normal bone density.
- Psoriatic arthritis remains within the differential although there is lack of distal joint involvement and new bone formation.
Case 7
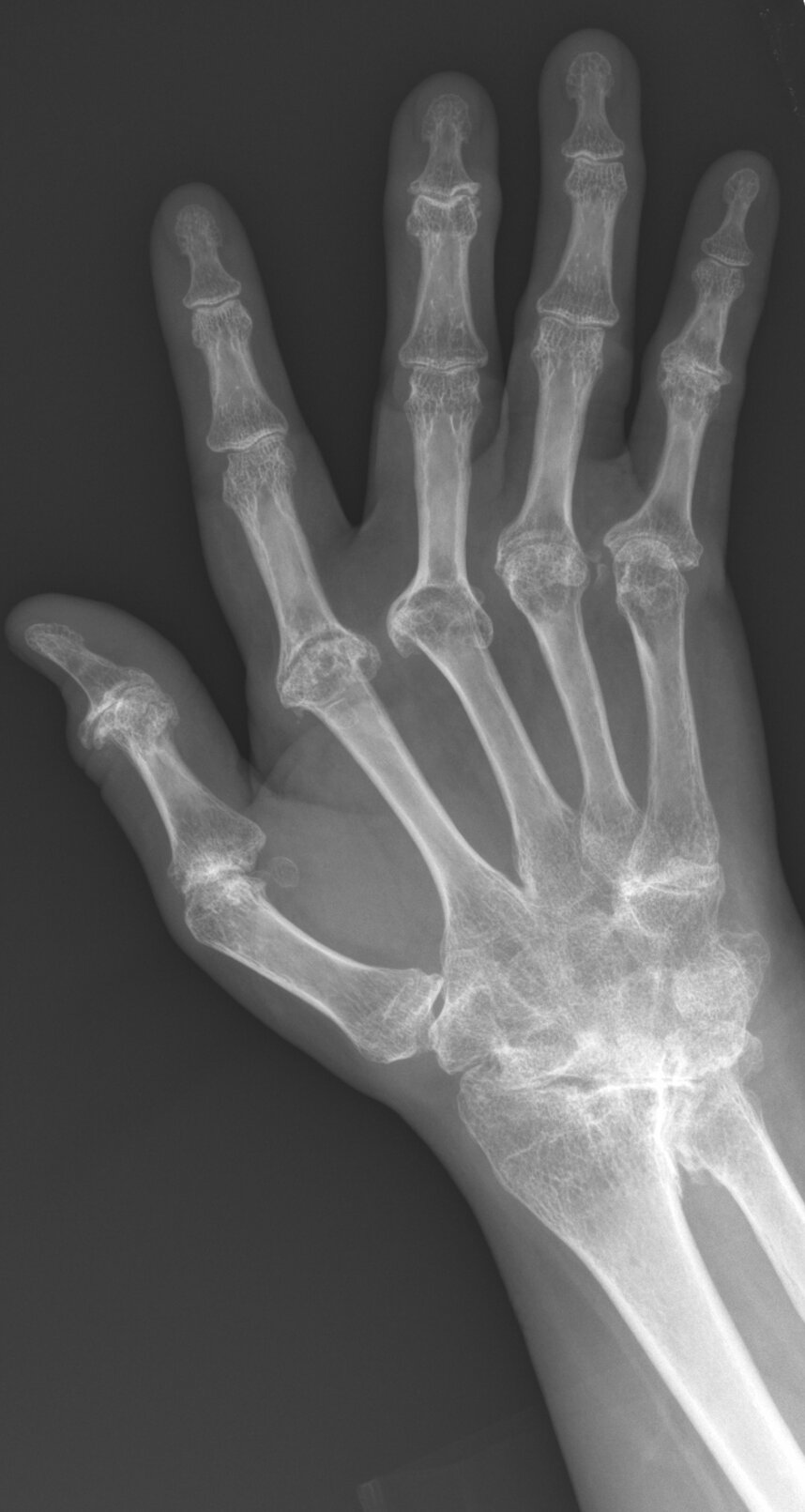
JABS Review
Joints:
- Diffuse carpal fusion, erosions with secondary degenerative disease at the distal radioulnar, radoiocarpal and MCP joints.
- Degenerative 1st IP joint.
Alignment:
- Mild ulnar translocation, ulnar deviation at 3rd MCPJ
Bone:
- Diffuse osteopenia
Soft tissue:
- Normal
Chronic Rheumatoid Arthritis
Teaching Point:
- Note lack of distal joint involvement or new bone formation.
- Compare with contralateral hand to assess for symmetry.
Case 8
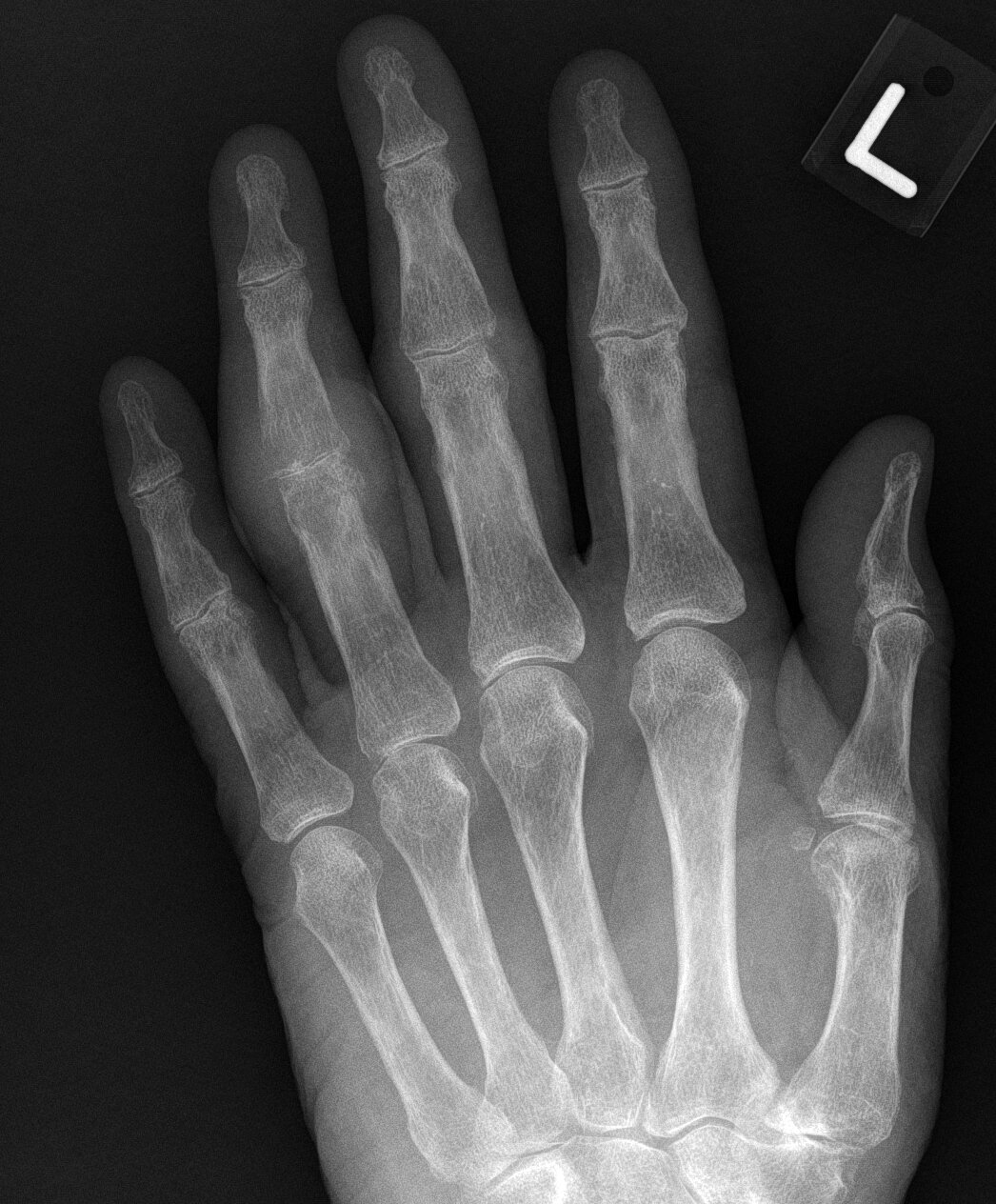
JABS Review
Joints:
- Moderate uniform joint space loss at 4th PIPJ, mild remaining PIPJs, non-uniform at MCPJs.
- No erosions
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Mild diffuse osteopenia, moderate periarticular osteopenia at the 2nd-4th PIPJs.
- There is a more defined subchondral lucencies head 4th proximal phalynx and ulnar margin base 4th middle phalanx with thinned overlying cortex without definite erosion (intraosseous gout).
Soft tissue:
- Soft tissue swelling of increased density at the 2nd-4th PIPJs, particularly the 4th without calcification, gout top
Gout, acute.
Teaching Point: The subchondral lucencies head 4th proximal phalynx and ulnar margin base 4th middle phalanx represent intraosseous gout
Case 9

JABS Review
Joints:
- Mild radioscaphoid, moderate to severe triscaphe and 1st CMC degenerative disease with joint space loss without erosions.
- Extensive chonedrocalcinosis TFC complex.
Alignment:
- Normal
Bone:
- Large well defined lucency with sclerotic margin distal radius in keeping with a massive subchondral cyst.
- Smaller subchondral cysts distal ulna , ulnar styloid and base 4th metacarpal.
- Ulnar positive variance without radiographic changes of ulnar abutment syndrome
Soft tissue:
- Normal
CPPD Arthropathy
Teaching Point:
- Crystal disease is associated with subchondral cyst which may large and out of context with degree degenerative disease as in this case.
- Given the size of cyst the patient is predisposed to fracture
Case 11
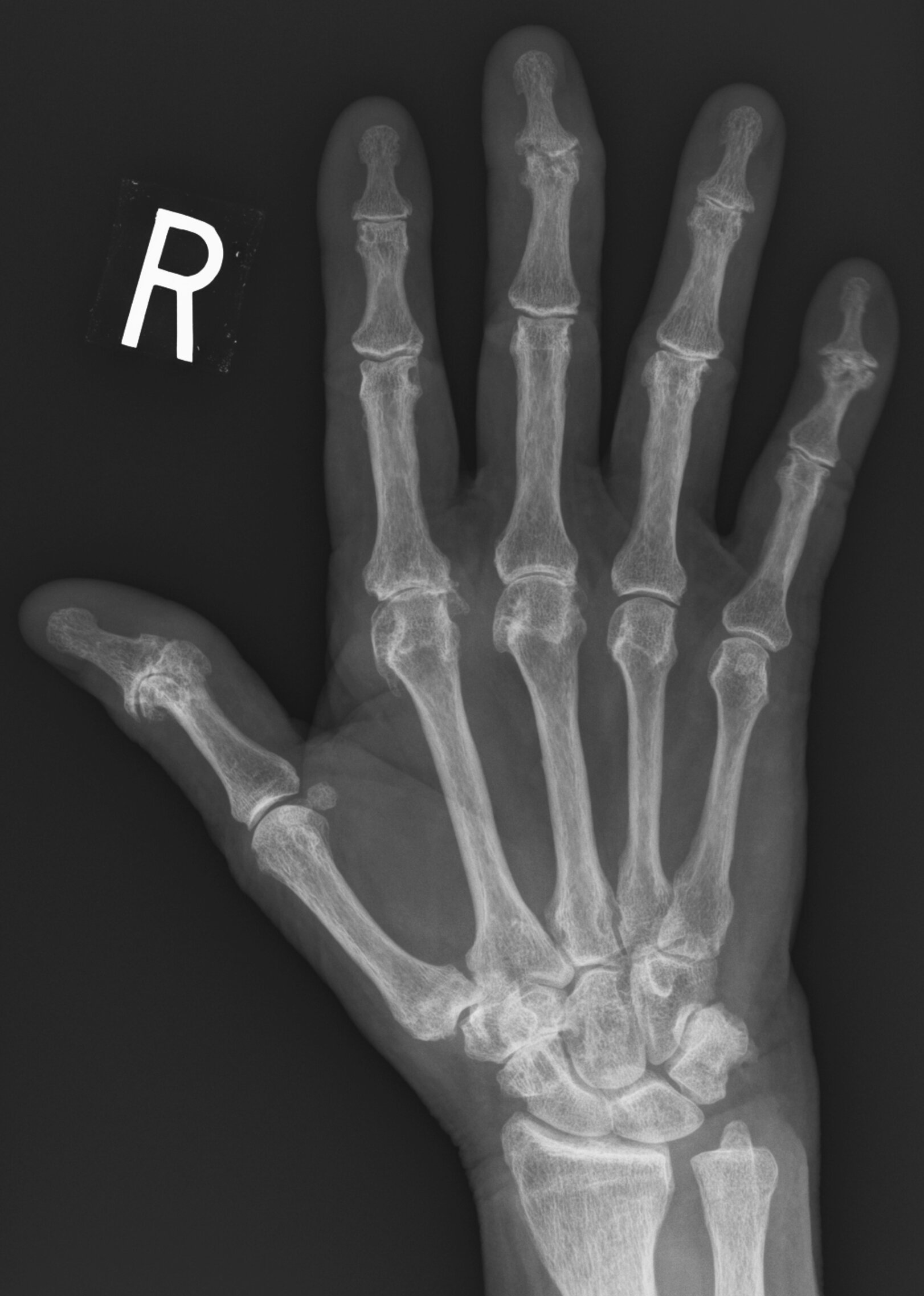
JABS Review
Joints:
- Joint space loss at 1st IP and DIPJs most pronounced at the 3rd DIPJ, with central erosions (3rd and 5th DIPJs) and osteophytosis, “gull-wing” appearance.
- There is also joint space loss at the MCPJs, most pronounced at the 2nd and 3rd with associated osteophytes, 1st CMC and triscaphe joints.
Alignment:
- Widened DRUJ.
- Miradial deviation at the 3rd DIPJ
Bone:
- Normal
Soft tissue:
- Mild soft tissue swelling 3rd DIPJ
Mixed disease.
- Erosive osteoarthritis DIPJs
- Osteoarthritis carpus and MCPJs suggesting CPPD arthropathy (chondrocalcinosis present on knee X-ray)
- DRUJ subluxation may relate to prior trauma (subchondral bone is normal, no erosions/periarticular osteopenia or soft tissue swelling)
Teaching Point: More than 1 pathology may be present.
Case 12
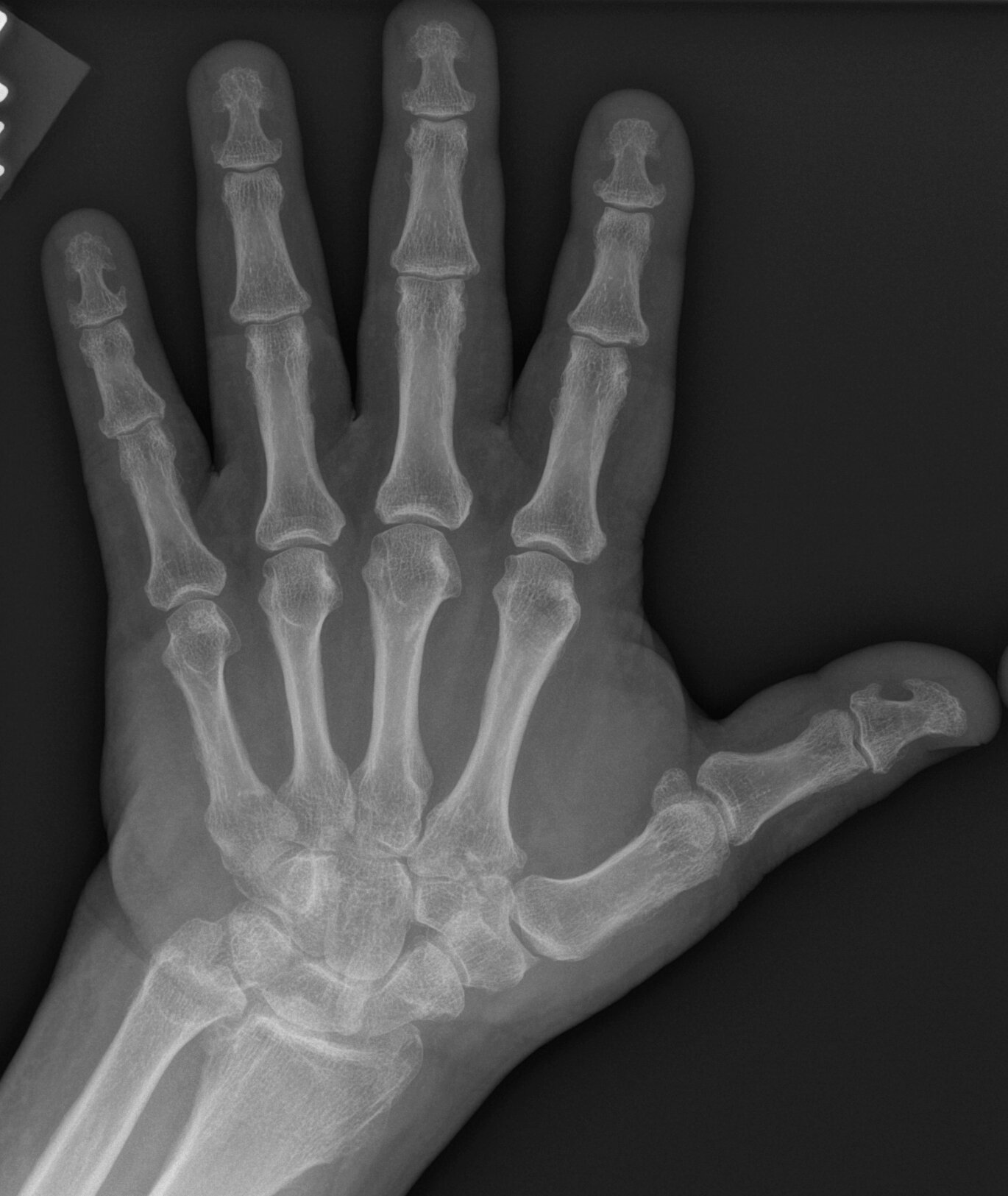
JABS Review
Joints:
- Early degenerative changes with joint space loss and osteophytosis at MCPJs, DRUJ, radoiocarpal joint.
- No erosions
Alignment:
- Normal, Spade-like hand
Bone:
- Prominent ungal tufts.
- Thickened metacarpals and phalanges.
- Normal bone density.
Soft tissue:
- Thickened soft tissues
Acromegaly
Teaching Point: Consider underlying aetiologies for degenerative disease including trauma, crystal depositional diseases etc.